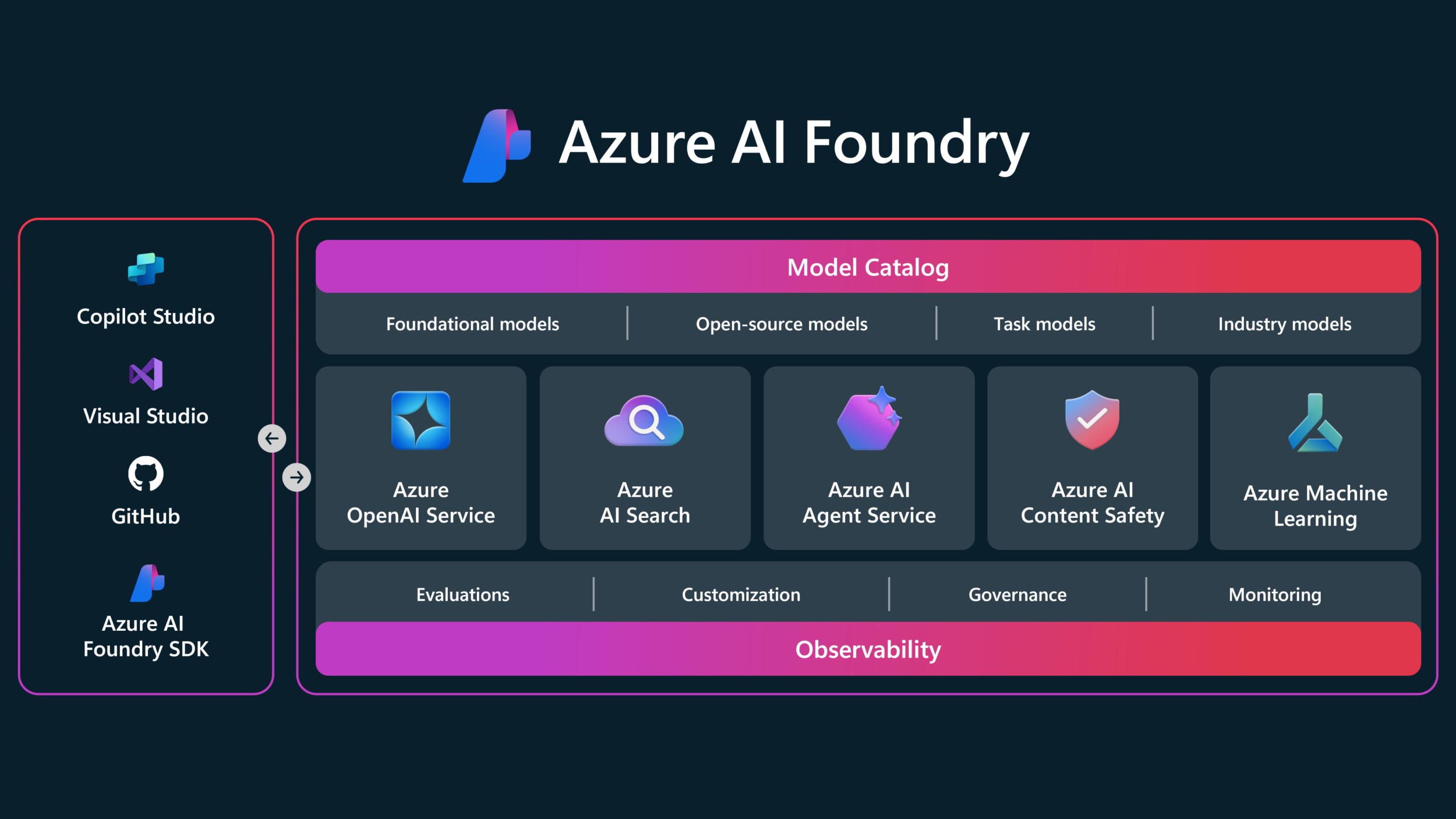
Azure AI Foundry Platform Best Practises
Azure AI Foundry best practises consideration - Platform team perspective
1. Governance
Establish clear organisation structure
Dedicated environments: Create dedicated Azure AI Foundry Hubs and projects for development, testing and production environments. This helps to isolate each environment workloads, connection and streamline the team/ user access management.
Business group alignment: Some organisations use Business unit based seperations. Create a seperate Azure AI Foundry for each business group to ensure autonomy, streamlines governance and cost tracking.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Microsoft Entra ID first approach: Always prioritize Microsoft Entra ID for authentication over API keys for Azure AI Foundry, Azure Open AI and other integrated Azure AI Services.
- Azure Role Based Access Control (RBAC): User least priviledge approach to assign permission to team/ user using the built-in roles or Azure RBAC custom roles (if any).
- Managed Identities: Use Managed Identities for service-to-service communication to eliminate the need for managing credentials.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Access: Use Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) for administrative access to AI resources to minimizing exposure time for high-privilege accounts.
- Conditional Access Policies: Configure risk based conditional access policies, to enforce MFA, trusted location or compliant devices for accessing Azure AI foundry resource.
Policy Enforcement
Utilise Azure policy to enforce organisational standards. For ex
- Restricting public network access for Azure AI Services.
- Diagnostic logs enablement and aggregation in central log analytics workspace.
Responsible AI Practices
- Content Safety: Apply Azure AI Content Safety controls across all models to prevent harmful content generation.
- Risk Detection: Use Defender for Cloud to identify AI workloads and assess risks pre-deployment. Conduct regular assessments of generative AI models.
2. Security Best Practices
Network Security:
Private Endpoints: Deploy Azure Private Endpoints for all Azure AI Foundry components and connected Azure AI services (Azure OpenAI, Azure AI Search, Azure Storage, Azure Key Vault). This ensures traffic remains on the Azure backbone network.
Disable Public Access: Wherever possible, disable public network access for your Azure AI Foundry resources and associated AI services.
Network Security Groups (NSGs) & Azure Firewall: Use NSGs to filter traffic at the subnet level and Azure Firewall for centralized network inspection and egress control for traffic originating from your AI VNet.
Web Application Firewall (WAF): If you expose AI applications via a web front-end, deploy Azure Application Gateway with WAF to protect against common web attacks.
Data Protection:
Encryption at Rest (CMK): For sensitive data and compliance, configure customer-managed keys (CMK) in Azure Key Vault for Azure AI Foundry workspaces, associated storage accounts, and any AI services that support it.
Encryption in Transit: All communication with Azure AI Foundry and its integrated services uses TLS 1.2 or higher by default. Ensure your client applications enforce this.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP policies at the data source level before data is ingested into AI services. Consider pre-processing data to redact or anonymize sensitive information.
Vulnerability Management:
- Continuous Scanning: Leverage Microsoft Defender for Cloud’s vulnerability assessment capabilities for any compute instances or custom container images used within Azure AI Foundry (e.g., Azure Machine Learning compute).
3. Monitoring Best Practices
Centralized Logging: Ensure all logs are aggregated to the centralised log analytics workspace.
Diagnostic Settings: Configure Diagnostic Settings for all Azure AI Foundry resources (hubs, projects, deployments) and connected Azure AI services to send AllLogs and AllMetrics to a central Azure Log Analytics Workspace.
Activity Logs: Monitor Azure Activity Logs for control plane operations (resource creation, modification, deletion) related to Azure AI Foundry.
Threat Detection & SIEM Integration:
Azure Sentinel: Connect your Log Analytics Workspace to Azure Sentinel. Leverage built-in Azure AI connectors, analytics rules (including those for unusual access, data exfiltration, or model misuse), and threat intelligence feeds.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud: Enable Defender for Cloud’s enhanced security features for relevant subscriptions and resources to receive security recommendations and threat alerts specific to AI workloads.
Performance and Quality Monitoring:
Azure Monitor Metrics: Monitor key performance metrics of your AI model deployments (e.g., tokens per minute, latency, error rates, model usage).
Responsible AI Observability: Utilize Azure AI Foundry’s evaluation tools and observability features to continuously monitor model quality, groundedness, relevance, safety, and potential drift in production. Set up alerts for deviations from expected behavior.
Alerting Strategy:
- Define actionable alerts based on security incidents, performance degradation, or cost anomalies. Prioritize alerts that require immediate human intervention.
4. Cost Management Best Practices
Understand Billing Model:
Azure AI Foundry costs are typically aggregated from the individual services you consume (Azure OpenAI models, Azure AI Services APIs, Azure Machine Learning compute, storage, etc.). Gaining knowledge on the token-based billing for generative AI models and the specific pricing for each component will help to understand costing better.
Azure Cost Management: Use Azure Cost Management tools to track and analyze costs related to your Azure AI Foundry deployments.
Budgets and Alerts: Create budgets at the subscription or resource group level and set up alerts for spending anomalies or overspending risks.
By adopting these best practices, organizations can confidently leverage the power of Azure AI Foundry to accelerate their AI journey, building secure, governed, observable, and cost-effective intelligent applications for the future.